LIVER DISEASES
A QUALIFIED AYURVEDA PRACTITIONER SHOULD BE CONSULTED TO ENSURE APPROPRIATE PROCEDURES AND MONITOR PROGRESSs
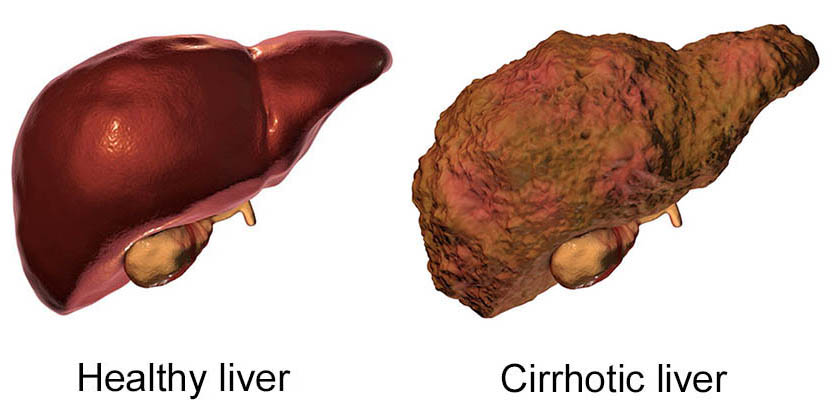
Liver Chrrhosis - Ayurveda treatment
AYURVEDIC TREATMENT FOR CIRRHOSIS
Replacement of normal liver tissues by fibrous tissues is called liver cirrhosis. In this condition liver becomes hardened and scarred. This can lead to liver failure and death. Liver cirrhosis may be considered as a stage which liver reaches after confronting with certain causative factors for prolonged period of time. There are no cure for cirrhosis but it can be treated with ayurvedic medicine from further progression.
WHAT IS LIVER CIRRHOSIS
Cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease in which healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue and the liver is permanently damaged. Scar tissue keeps your liver from working properly. The scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and slows the liver's ability to process nutrients, hormones, drugs and natural toxins (poisons). It also reduces the production of proteins and other substances made by the liver. Cirrhosis eventually keeps the liver from working properly. Late-stage cirrhosis is life-threatening. In advanced stage, liver cirrhosis can lead to ascites, which is accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
4 STAGES OF CIRRHOSIS
Cirrhosis of the liver is a disorder in which healthy liver cells are gradually replaced by scar tissue. It is a progressive illness that might take several years to develop.
Cirrhosis is classified into four stages that include:
Stage I: Steatosis
- The first stage of liver disease is characterized by inflammation of the bile duct or liver.
- As the body strives to fight against the disease or infection, abdominal discomfort is frequently the first symptom of inflammation.
- If this inflammation is not managed, it might cause damage to the liver, exacerbating the illness.
- Symptoms and inflammation are generally curable during stage I and can prevent liver disease from escalating to stage II.
Stage II: Scarring (fibrosis) of the liver due to inflammation
- Many people with liver illness don't realize they have it until they are at stage II or III because the first symptoms generally go unreported.
- In stage II, scarring or inflammation (damage) begins to obstruct the natural flow of blood in the liver.
- This causes the liver to be unable to function properly, but with treatment, the liver may still be capable of recovering, avoiding more damage, and slowing the progression of the liver disease.
Stage III: Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis develops due to the advancement of liver disease, mainly due to lack of
therapy, in which scar tissue replaces good tissue in the liver.
- This process occurs when healthy liver cells have been destroyed over time (often
several years) by a progressive illness or infection.
- This causes permanent scarring of the liver, causing it to become hard and lumpy.
- The liver will eventually be unable to function because the growing scar tissue will make
blood flow through the portal vein and into the liver impossible.
- When this blood is prevented from accessing the portal vein, it can flow into the spleen,
causing additional problems.
Stage IV: Liver failure or advanced liver disease or hepatic failure
- Failure of the liver during the disease's ultimate stage will signify the end of the liver's functioning. This will necessitate quick medical intervention to avoid fatalities.
CAUSES OF LIVER CIRROHSIS
Common causes of liver cirrhosis include:-
Excessive Consumption Of Alcohol
The liver purifies the toxins such as alcohol in the blood. If consumption of alcohol is too high, the liver has to overwork, and the liver cells are eventually damaged. In comparison to healthy individuals, heavy and long time drinkers are more likely to develop cirrhosis.
The alcohol – induced liver disease progresses in three stages. First, there is a fatty liver with the build-up of fat in the liver. In the next stage, due to alcoholic hepatitis, the liver cells swell up. About 10 to 15% of heavy drinkers develop cirrhosis.
Hepatits
There are different strains of hepatitis as per the viruses. Hepatitis C is a blood-borne infection that damages the liver and slowly leads to cirrhosis. Hepatitis B and D may also lead to cirrhosis.
Non – Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
The accumulation of fat in the liver may also happen due to other reasons than excessesive consumption of alcohol. In the early stages, there is inflammation that progresses to scarring and later on cirrhosis. It is common in people who have high levels of fat in their blood, obesity, diabetes and high blood pressure.
Autoimmune Hepatitis
In some cases, the body's immune system becomes overactive and starts attacking the healthy organs of the body in the absence of foreign substances. If the liver is attacked, the patient developed cirrhosis.
Genetic Diseases
Some inherited conditions such as Wilson's disease or hemochromatosis may also lead to cirrhosis. In wilson's disease, copper accumulates in the liver and other parts of the body. Whereas hemochromatosis iron accumulates in the liver or other parts of the body. Besides, the above, cystic fibrosis, genetic digestive disorder, alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency, infections such as brucellosis, scarring and hardening of bile ducts and certain medications including isoniazid and methotrexate may also cause liver cirrhosis.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS OF CIRRHOSIS
| SIGNS & SYMPTOMS |
| Itchy skin |
Yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes |
| Dark urine |
Upper right-sided abdominal tenderness |
| Unexplained flu-like symptoms |
Abdominal pain and tenderness |
| Symptoms are sometimes worse when an episode of significant drinking, and have a tendency to vary with the severity and progression of the unwellness. Generally symptoms don't gift themselves till the unwellness is comparatively advanced. |
| Ascites (excess fluid between the membranes lining the abdomen and abdominal organs) |
| Dry mouth / excessive thirst |
Weight gain because of pathology |
| Abnormally dark or light-weight skin |
Altered level of consciousness |
| Breast development in males |
Difficulty concentrating |
| Bloody or dark, black, or tar-like internal internal organ movements |
| Fluctuating moods |
Light-headedness or fainting |
| Hallucinations |
Redness on feet or hands |
| Impaired short- or memory |
Slow, sluggish, lethargic movement |
| Rapid pulse rate once rising to a standing position |
Vomiting blood or a sludge-like material |
DIAGNOSIS
The main test from with the help of which can access liver problems are as follows:
- Aminotransferases – AST and ALT are moderately elevated, with AST > ALT. However, normal aminotransferases do not preclude cirrhosis.
- Alkaline phosphatase – usually slightly elevated.
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase – Correlates with AP levels. It is typically much higher in chronic liver disease from alcohol.
- Bilirubin – May elevate as cirrhosis progresses.
- Albumin – Levels fall as the synthetic function of the liver declines with worsening cirrhosis since albumin is exclusively synthesized in the liver.
- Prothrombin time – Increases since the liver synthesizes clotting factors.
- Globulins – increased due to shunting of bacterial antigens away from the liver to lymphoid tissue.
- Serum sodium – Hyponatremia due to inability to excrete free water resulting from high levels of ADH and aldosterone.
- Thrombocytopenia – Due to both congestive splenomegaly as well as decreased thrombopoietin from the liver. However, this rarely results in platelet count < 50,000/mL.
- Leukopenia and neutropenia – Due to splenomegaly with splenic margination.
- Coagulation defects – The liver produces most of the coagulation factors and thus coagulopathy correlates with worsening liver problems.
The following tests may be used to evaluate the liver :
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
- CT scan or MRI (MRCP) scan
- Laparoscope
- Endoscopy to check for abnormal veins in the esophagus or stomach
- Radioisotope liver/spleen scan
- A liver biopsy confirms cirrhosis. Some patients will be screened for liver cancer.
COMPLICATIONS OF LIVER CIRROHSIS
Here are the complications of liver cirrhosis. These conditions generally appear because of the lack of proper treatment for liver cirrhosis.
Bruising and Bleeding
As liver dysfunction progresses, the production of a protein needed for the blood clotting slows down or stops and results in bruising or bleeding.
Portal Hypertension
Normally, the blood from spleen and intestine is carried through the portal vein to the liver. Due to liver cirrhosis, the normal flow of blood slows and increases the pressure in portal veins leading to portal hypertension.
Ascites and Edema
As liver damage progresses, the fluids starts collecting in the legs and abdomen. Ascites due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen may lead to bacterial peritonitis, which is a very serious infection.
Splenomegaly
Due to portal hypertension, the spleen enlarges and holds the white blood cells and platelets. This decreases the number of these cells in the blood.
Esophageal Varices and Gastropathy
Due to portal hypertension, the blood vessels in the esophagus enlarge and lead to varices. In addition, the blood vessels in the stomach enlarges and leading to gastropathy. Enlarged blood vessels burst and lead to serious bleeding in the upper stomach and esophagus that requires emergency treatment.
Jaundice
Liver dysfunction results in the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood and causes yellowing of Eyes, Skin and Darkening of Urine
Hepatoencephalopathy
As the liver fails to remove the toxins in the blood, the toxins eventually accumulate in the brain. The build-up of toxins in the brain termed hepato-encephalopathy decreases mental function and may lead to a coma
Sensitive to Medication
The ability of the liver to filter the medications from the blood slows down. The medication stays longer t5han the expected time and builds up in the body. The patient becomes sensitive to medication and is subjected to the side effects.
Other complications of liver cirrhosis include liver cancer, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes. It may also lead to lung and kidney failure.
Earlier you opt for the Ayurvedic treatment for liver cirrhosis better results you can expect
AYURVEDIC TREATMENT FOR CIRRHOSIS
(1) PANCHAKARMA & THERAPIES FOR CIRRHOSIS OF LIVER
Pancha karma means five purification process or therapies. Ayurveda treatments give a bigger number of accentuation on aversion than cure. That is the reason counteractive action is dependably superior to cure. As in liver cirrhosis basically the pitta dosha is imbalanced so firstly it is been balanced. Panchkarma treatment is not required in this disease only medicines are sufficient
Apart from internal medication, if there is severe imbalance of the doshas, Panchakarma treatments like Virechana is prescribed to eliminate the excessive pitta dosha. Vamana may also be given in case of an aggravated kapha dosha. Expelling the excessive kapha and pitta dosha helps in activating metabolism.
(2) AYURVEDIC TREATMENT
Ayurveda treatment factors in the level of damages done to the liver and other complications. The first goal of treatment is to stop further scarring of liver tissue with nectar like herbs of Ayurveda, as the scarring of liver tissue stopped, liver functions improve gradually. In mild to moderate liver damage cases, Ayurveda definitely helps to stop further liver damage. A clinical studies reported Snehapana (therapeutic oral administration of lipids) followed by virechana (purgation) effective in treating cirrhosis. This was done after an initial course of nityavirechana (dialy purgation). Once this course is over, the doctors administered pippali (piper longum) to rejuvenate liver cells. This therapy was effective in resolving ascites and lower limb oedema, without any instance of recurrence.
WE HAVE A MADE A UNIQUE KIT MADE UP FROM AYURVEDIC NATURAL COMBINATIONS. WITH THE HELP OF THIS THE MAIN SIGN AND SYMPTOMS LIKE JAUNDICE, ASCITES BEGIN TO REDUCE FROM THEIR PEAK LEVEL. THE MEDICINES ARE HERBAL FORMULATIONS BASED ON ANCIENT SCIENCE AND MODERN RESEARCH. THE VARIOUS HERBS USED IN AYURVEDA ARE LIVER PROTECTIVE, CORRECTIVE AND HAVE REGENERATING EFFECT ON THE DEAD LIVER CELLS.
THE MEDICINES PROVIDE A NATURAL DEFENSE TO LIVER FROM TOXINS OF FOOD, WATER, ALCOHOL OR DRUGS. THE HERBAL AYURVEDIC LIVER CIRRHOSIS KIT STIMULATES THE LIVER AND THUS PRODUCES MORE BILE. IT INCREASES THE APPETITE NATURALLY. THIS MEDICINES PROVIDES A NATURAL DEFENSE TO LIVER FROM TOXINS OF FOOD, WATER, ALCOHOL OR DRUGS.
(3) HERBS FOR CIRRHOSIS OF LIVER
Kalmegh: Kalmegh, the active constituent isolated from the plant Andrographis paniculata or Kalmegh, showed considerably enlarged % viability of the hepatocytes. For hundreds of years, Andrographis has been a vital herb within the Ayurveda.
Punarnava: An alcoholic extract of the whole plant Punarnava given orally exhibited hepatoprotective activity. The extract additionally made a rise in traditional digestive juice flow suggesting a powerful choleretic activity.
Guduchi: Outstanding leads to individuals affected by jaundice are obtained employing a herb referred to as Guduchi or Tinospora Cordifolia used the herb in malignant hindering jaundice.
Katuki: Katuki or Picrorrhiza Kurroa is one of the herbs they suggest supporting the liver.
Baheda: Elicited physiological and organic chemistry alterations within the liver. Our results make sure the presence of hepato protecting activity in altered parameters.
DIET & LIFESTYLE FOR CIRRHOSIS
A patient must take expert opinion of an Ayurveda for the right treatment of liver cirrhosis.
- Eat a well-balanced, low-fat diet. A well-balanced healthy diet consists of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains.
- Don't eat raw seafood, especially oysters and clams. These foods can contain a bacteria that can cause serious illness. Eat a well balanced and nutritious diet that contains a lot of fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Opt for sources of good fats such as nuts, seeds, avocado, and olives.
- Avoid packaged food items with added preservatives, including pickle .
- Papaya seeds additionally work effectively in natural process liver cirrhosis.
- To enhance the potency of the drink add three hundred milliliter of juice to two hundred milliliter of spinach juice.
- Radish also cures an individual affected by liver disease of the liver.
- The juice of the leaves of the herb referred to as eclipta alba has evidenced priceless in liver disease of the liver.
- Cut back on the amount of salt in your diet
- Kutki or Picrorhiza kurroa additionally plays in natural process the liver disease of liver by Ayurvedic methodology.
- After the fruit and milk diet, the patient should embark upon a well-balanced diet, consisting of seeds, nuts, grains, vegetables, and fruits with stress on raw, organically fully grown foods.
- All fats and oils should be excluded from the diet for many weeks.
PREVENTION OF CIRRHOSIS
The prevention of fatty liver lies in a simple and healthy lifestyle. It includes both diet and daily routine. Here are some additional points that may provide better guidance:
- If you have a long history of alcohol consumption, then you must join a reform program or therapy to quit alcohol altogether.
- If you are diabetic and have a doctor-prescribed diet chart, please stick to it.
- Always keep a check on your cholesterol, high blood pressure, blood sugar, and triglycerides levels. It doesn't matter if you are diabetic or not, these levels should always stay within permitted limits.
- Make it a routine to exercise for at least 30 minutes every day. It will help to avoid several problems including a fatty liver.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess body fat can damage your liver. Ask your healthcare provider for a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Quit smoking if you smoke.
Healthy liver practices:
- Avoid high-risk behaviors that can lead to infection with hepatitis B or C, such as having unprotected sex.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B. If you already have hepatitis, ask your provider if drug treatment is appropriate for you.
- Get your annual flu shot and ask if a pneumonia vaccine makes sense for you (people with cirrhosis are more likely to get infections).
- Avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen ] indomethacin, celecoxib and aspirin and high doses of acetaminophen. Acetaminophen can be taken safely at a dose up to 2,000 mg daily. These drugs can cause or worsen liver function.
Take all medications and keep all appointments as recommended by your healthcare provider. Ayurvedic treatment varies from person to person and therefore one must consult an expert and not try these ayurvedic medicines for liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
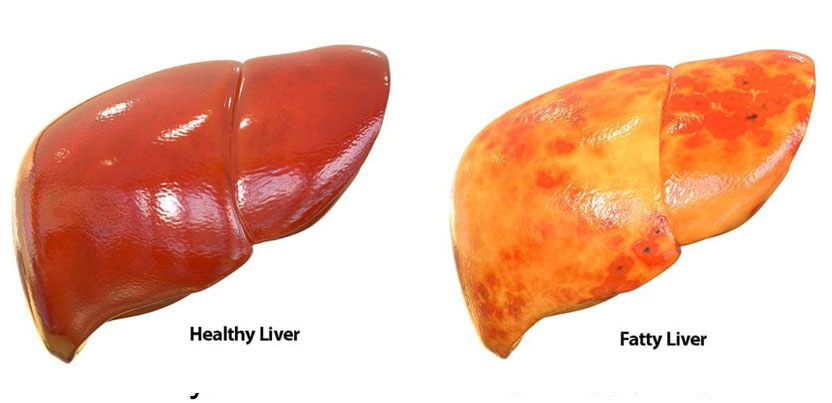
FATTY LIVER - AYURVEDIC TREATMENT
The liver is the body's largest gland and heaviest organ. It is a highly vascular organ that receives approximately 30% of resting cardiac output. The liver is the organ in which virtually all nutritional substances are metabolised. Because the liver is so important in fat metabolism, it is the most common site for fat accumulation. Depending on the cause and extent of the accumulation, fatty change can be mild and reversible or severe, resulting in irreversible cell injury and cell death. Fatty liver is caused by disruptions in lipid metabolism in the liver caused by a variety of etiological factors.
WHAT IS FATTY LIVER
Hepatic steatosis also known as Fatty liver in common terms describes the buildup of fat on liver. It's normal to have small amount of fat on the liver, but too much of fat on the liver could lead to a health problem which could damage the liver.
The liver is widely responsible for a variety of functions in the human body. It filters harmful substances from the blood. It is also the second largest organ in the body. When the liver contains more than 5 percent fat then it should be diagnosed.
TYPES OF FATTY LIVER
Fatty liver disease is categorized into three main types :
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The fat build-up, in this case, is due to an unhealthy diet and lots of carbohydrates. Usually, it is not inflammatory in nature and doesn't result in too many complications. But if the patient experiences inflammations despite being non-alcoholic, it is known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver: When the fat deposition crosses the healthy limit due to excess alcohol consumption, the problem is known as alcoholic fatty liver disease. If left untreated or ignored for long, it may result in wounds in the liver or liver damage. Patients suffering from this problem must quit alcohol immediately.
- Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy: It is a very rate complication but a serious one. The exact cause of this problem is not known. It needs to be treated as soon as the problem is diagnosed. Any delays may pose serious health risks for both the mother and the baby.
CAUSES OF FATTY LIVER
There are many factors such as high body weight, high processed sugar diet, diabetes, high triglycerides, genes, liver infections and low physical activities also plays an important role in fatty liver. Nowadays, people with alcohol consumption or disorder are common to identified fat on liver. In scientific words, when human body creates too much fat and that excessive fat stored in liver cells, is accumulated as fatty liver disease. While in few cases side effects of medicines such as trexall, nolvadex, pacerone and depakote could lead to fatty liver.
SYMPTOMS OF FATTY LIVER
In general fatty liver has no associated symptoms. According to studies, it is believed that excess fat in the liver increases inflammation and you may have symptoms such as:
- Weight loss
- Physical weakness
- Fatigue & Tiredness
- Confusion
- Poor appetite
- Swelling in the upper abdomen
Discomfort in upper abdomen in case of severe fatty liver which could lead to liver failure, patients could have symptoms such as:
- Genetic inheritance
- Jaundice
- Abnormal bleeding
- Enlarged fluid filled abdomen
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Tarry Stools
- Pain in the abdomen
- Yellow eyes & Skin
- Difficulty focusing, memory loss, Confusion & Hallucinations
- Itchy Skin
DIAGNOSIS
Still, an ultrasonography scan (USG) confirms the diagnosis of fatty liver. Our Clinics follows a holistic approach to provide effective relief in all these symptoms with Fatty Liver Treatment in Ayurveda. Non-alcoholic fatty liver and Alcoholic fatty liver are the two clinical subtypes of the disease.
COMPLICATION OF FATTY LIVER
Fatty liver disease doesn't cause major problems for most people. However, it can turn into a more serious problem if it progresses into cirrhosis of the liver. Untreated cirrhosis of the liver eventually leads to liver failure or liver cancer.
The problem occurs when you have fatty liver with obesity, high cholesterol levels, high BP, or PCOS or hormonal imbalance and together they can cause metabolic syndrome.
TREATMENT FOR FATTY LIVER IN AYURVEDA
The goal of fatty liver treatment is to reduce or eliminate the cause of fatty liver. People should, for example, Quit drinking alcohol, stop fatty food, Stop using any prescription that could cause fatty liver , Lose weight ,Control diabetes or lower triglyceride levels etc. A 5% reduction in body weight can lower liver fat content, a 7% reduction can reduce inflammation and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and a 10% reduction can help reverse scarring and fibrosis.
(I) PANCHAKARMA (VIRECHANA & VAMANA ONLY) TREATMENT
Ayurveda known for its safe and effective medication has a great potential in treating Fatty Liver. Ayurveda describes the liver as a site of Pitta. Pitta in the liver helps in the proper digestion and energy transformation. Ayurvedic treatment for fatty liver disease aims to correct the vitiated Pitta dosha. Vamana and Virechan are robust cleansing procedures for the liver. Virechana being the most suitable Detox-Shodhana Karma. Also effective and safe Hepatoprotective herbs to treat any kind of liver disease.
Virechana
- Virechana is a purgation procedure, which is specifically performed to eliminate excess pita, it also leads to elimination of excessive Vata and Kapha.
- It is indicated in the treatment of many health conditions including Asthma, disorders of large intestine, disorders caused by vitiation of the Rakta Dhatu, insanity, gastrointestinal disturbances and Pitta-related conditions.
- Hot liquids or solid foods, meat soups and food containing fatty materials are given to the patient before Virechana.
- Herbs for this procedure are decided according to the patient's condition
- After undergoing Virechana, people experiencing lightness in the body and an improvement in appetite.
- Virechans is known as the Shodhana karma for treating liver conditions. Therfore, it can be usedful in treating kamala and fatty liver
Vamana (Medical Emesis)
- In the Vamana procedure, excess pitta and Kapha and Kapha Doshas are eliminated from the body via body route.
- Vamana is indicated for Anorexia, Asthma, Petic Ulcers, Sinusitis and Kapha related diseases.
- Milk, oily foods, animal meat and fatty foods are given to increase Kapha in the body before performing this procedure.
- Vaman is beneficial in reducing weight, total cholesterol levels and total triglycerides. Therefore, it can help treat fatty liver caused due to obesity.
- This procedure reduces urea levels, serum and help improve liver function.
(II) AYURVDIC MEDICINES FOR FATTY LIVER
a.Vasaguduchyadi Kashaya
- Vasaguduchyadi Kashaya is an Ayurvedic formulation that is prepared using Triphala (a combination of Amalaki (Indian Gooseberry), Vibhitaki (Belleric Myrobalan) and Haritaki), Neem, Guduchi and eight other herbal ingredients.
- This medicine is used to treat Jaundice and Anaemia
- It has hypolipidaemic, haematinic and hepatoprotective properties that make it useful in the management of liver conditions like NAFLD as well.
b. Pippalyasava
- This formulation is prepared from 26 herbs including Ela(Cardamom), Vidanga (False Black Pepper), Turmeric, Pippali, Maricha (Black Pepper), Jaggery, Jatamansi (Muskroot) and Amalaki.
- It is indicated in the treatment of Piles, Spleen disorders, Pthiasis, Sprue, Anorexia, General fatigue and Flatulence and also helps to increase appetite.
- The hepatoprotective properties of this herb, which makes it useful in the treatment of liver diseases like NAFLD
c. Arogyavardhini Rasa
- Arogyavardhini Rasa, as the name suggests, is used to promote the overall Arogya (Health)
- It brings about a balance between the three doshas and mentioned in the context of Kushtha (Skin Diseases) and Yakrut (Liver) conditions.
- This herbo-mineral formulation included Paras (Mercury), Gandhak (Brimstone), Shilajatu (Asphaltum), Tamara Bhasma (Calcined Preparation of copper), Chitraka (Leadwort), Katuki, Abhraka Bhasma (Calcined preparation of mica), Guggulu and some other ingredients.
- This medicine is included in the treatment of Worm infections, Agnimandya (Weakened Digestive fire), pleehadosha (Spleen conditions), medoroga (Diseases of the Meda Dhatu) and Prameha (Diabetes).
- Arogyavardhini Rasa has antioxidant properties, which helps improve liver function and aids in the management of conditions like Jaundice and NAFLD
Various Ayurveda formulations for Fatty liver are mentioned in classical texts which can widely be used for this purpose like Pippali Churna, Patoladi Churna, Mahasudarshana Churna, Rohitaka choorna , Agnitundi Vati, Arogyavardhini Vati, Patola katurohinyadi Kashaya, Rohitakarishta, Pippalyasava, Kumaryasava, Kalameghasava, Yakrit-Plihari Loha, Kutaki, Bhumyamalaki, Triphala, Aloe vera, and many others ensure liver support and strengthening can be taken consulting Ayurveda physician.
THIS TREATMENTS VARY BASED ON NUMEROUS FACTORS AND AN INDIVIDUAL'S PRAKRITI (CONSTITUITION), CONSULT A QUALIFIED AYURVEDIC DOCTOR FOR APPROPRIATE MEDICATIONS AND TREATMENTS FOR YOUR SPECIFIC COMPLAINTS.
(III) HERBS FOR FATTY LIVER
a. Guduchi
- Guduchi acts on the digestive and circulatory systems
- It is a bitter herb with tonic properties that helps in the strengthening the overall body system. Giloy also promotes tissue regeneration.
- It stimulates the natural immune responses in body and is used in the treatment of Malarial Fever, Piles, Skin Conditions, Jaundice, Dysentery, Constipation and Gout.
- Guduchi is known as the best Dosha pacifying herb for NAFLS management.
- You can take it in the form of powder, extract or as per your Physician's direction.
b. Bhumiamalaki
- Bhumiamalaki acts on the urinary, digective and reproductive systems.
- It is used in the treatment of Jaundice, Urogenital Diseases, Gonorrhoea, Dyspepsia, Colitis, Dysentery, Ulcers, Skin conditions, Tonsillitis, and Bleeding gums.
- Bhumiamalaki has astringent and stomachic properties that make it useful for treating health conditions.
- It is especially recommended for the treatment of liver conditions like Jaundice and NAFLD
- You can take Bhumiamalaki in the form of a pill, infusion, Powder, Poultice or as per your physician's direction.
c. Katuki (Kutki)
- Katuki has laxative, cholagogue (promotes expulsion of bile) and stomachic peoperties and it acts on the excreatory, digestive, nervous, female reproductive and circulatory systems.
- This herb helps treat Skin Conditions, Metal Toxicity, Bilious Fevers, Paralysis and Constipation arising from the Small Intestine And Malaria
- It akso has hepatoprotective properties that make it useful in the treatment of liver conditions like Jaundice, Viral Hepatitis and NAFLD.
- You can take Katuki in the form of a pill, powder, extract, tincture or as per your physician's direction
d. Haritaki (Chebulic Myrobalan)
- Haritaki acts on the female reproductive, digestive, respiratory and excretory systems.
- It has laxative, rejuvenating, nervine, tonic and astringent properties and is known for improving longevity, memory, intellect and digestion
- Haritaki is used to treat Abdominal Distention, Jaundice, Tumours, Rheumatism, Asthma, Colic, Ulcerated Gums, Itching, Diarrhoea, Spleen condtions and Paralysis.
- It is also effective in the management of liver conditions like NAFLD
- Haritaki shows therapeutic effects in the people with obesity as well. Therefore, it is useful to treat fatty liver caused due to obesity.
- You can take Haritaki in the form of powder, gargle, paste, decoction or as per your Physician's direction.
e. Pippali (Long Pepper)
- Pippali has aphrodisiac and pain-releiving properties and it acts on the respiratory, digestive and reproductive systems.
- The herb is used for treating Cough, Kapha disorders, Sciatica, Paralysis, Asthma, Epilepsy and Worm Infections.
- Pippali makes an important component of various ayurvedic formulations due to its hepatoprotective properties. Ot contains alkaloids like piperine, which promotes regeneration of liver cells. It is also effective against many liver conditions like Hepatobiliary Disorders, Liver Cirrhosis and Fatty Liver.
- You can take Pippali in the form of Oil, Powder, Infusion or as per your Physician's direction.
Take all medications and keep all appointments as recommended by your healthcare provider. Ayurvedic treatment varies from person to person and therefore one must consult an expert and not try these ayurvedic medicines for liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
HOW CAN I REDUCE MY FATTY LIVER?
When it comes to fatty liver there are few steps which can be followed to reduce the fat on the liver are -
- Weight loss - fatty liver is a kind of condition which took place when fat levels in the body increases due to unhealthy lifestyle. In such cases, doing physical activity is something one must do and should follow a healthy regime to lose weight.
- No to alcohol - in case of people who use to intake alcohol in large quantity are recommended to avoid alcohol as it lead to harmful effects on health.
- Balanced diet - eating healthy and timely food is the key of good health. It also applies on people having fatty liver.
- Control your sugar - people who are diabetic are needed to be careful. Such patients should control their sugar levels and keep a check on it as well.
DIET & LIFE STYLE FOR FATTY LIVER
Ayurveda suggests certain types of food which are extremely important to add in the diet of Fatty liver patient. Vegetables which are bitter in taste, astringent and light to digest are good for fatty liver cases
- Include curry leaves, Methi leaves, red rice, Green gram, Pomegranate, Dry Fruits, Garlic, Snake Gourd, Coriander, Bitter Gourd, Ginger, Buttermilk, Barley, Orange, Raisins, Drumstick and a Gruel prepared from Panchakola (5 spices) and Trikatu (a combination of the three Acrids – Pipplai, Shunthi (Dried Ginger) and Maricha) in your diet.
- Eat freshly prepared foods
- Take your meals on time
- Consume a low fat and high fibre diet
- Drink at least eight glasses of lukewarm water per day
- Exercise for 30-45 minutes a day is crucial for active metabolism.
- Practice Pranayama and Yoga Asanas like Gomukhasana and Dhanuraasana.
- Eat a nutrient-rich, plant-based, low-calorie, low-fat natural diet and which is in high fibre. Exercise for 30-45 minutes a day is crucial for active metabolism.
- 30 ml Aloe Vera juice in the morning and 1 tsp of Triphala Choorna at night can be practised regularly to avoid fatty liver disease.
Foods to Promote Healthy Liver
- Whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat, rye, and oats to be made part of the person's regular diet. Organic fruits and vegetables that are rich in fiber will benefit a fatty liver sufferer.
- If meat cannot be avoided, the person will need to switch to fat-trimmed meats and chicken. Seafood like prawn, salmon, sardine, tuna, etc. which are rich in essential fatty acids may also be consumed by the sufferer.
- For regular cooking, oils that contain omega-3 fatty acids are recommended for the sufferer. The best choice would be cold-pressed olive oil.
Foods to Be Avoided in Fatty liver
- Refined carbohydrates like white rice, white bread, noodles, and pasta to be removed from the person's diet.
- Altogether avoid the non-vegetarian diet, fried food, bakery food items, aerated cold drinks, fast food, and other processed foodstuffs.
- Processed junk foods contain excess greasy fats and thus needs to be removed. Breakfast cereals are also processed highly and should be avoided. Likewise, baked goods like cakes, cookies, scones, puff pastry, etc., require excess fats for baking purposes and needs to be eliminated by the sufferer.
- Deep fried sweet and savories also to be avoided by the person. Meat, especially red meats like lamb, pork and beef, and meat products that contain animal fats needs to be avoided.
- Dairy rich products like cheese, butter, margarine, mayonnaise, ice-creams and fruit yogurt also to be avoided
PREVENTION OF FATTY LIVER
The prevention of fatty liver lies in a simple and healthy lifestyle. It includes both diet and daily routine. Here are some additional points that may provide better guidance:
- Do not consume cauliflower, Black Gram, Curd, Potatoes, Pickle, Milk, Yellow Gram, Meat preparations, Full-fat Milk, Fish, Basmati rice, Artificial Sweeteners, Chocolates, Jams and Ice creams.
- Avoid aerated drinks, bakery food items, excessively spicy fatty foods
- Avoid eating sour, salty foods
- Do not eat canned and preserved foods and junk food
- DO not follow a sedentary lifestyle
- DO not drink alcohol
- Do not smoke
- DO not overeat
- DO not sleep during day
- If you have a long history of alcohol consumption, then you must join a reform program or therapy to quit alcohol altogether.
- Focus on maintaining a healthy weight.
- If you are diabetic and have a doctor-prescribed diet chart, please stick to it.
- Always keep a check on your cholesterol, blood sugar, and triglycerides levels. It doesn't matter if you are diabetic or not, these levels should always stay within permitted limits.
Take all medications and keep all appointments as recommended by your healthcare provider. Ayurvedic treatment varies from person to person and therefore one must consult an expert and not try these ayurvedic medicines for liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
JAUNDICE - AYURVEDIC TREATMENT
AYURVEDIC TREATMENT FOR JAUNDICE
Ayurvedic treatments have been traditionally used to treat various types of liver disorders successfully, including all types of jaundice, and even now, more than 50% of the Indian population relies on Ayurveda for the treatment of liver diseases. This is because toxicity levels of medications used in Ayurveda are low as compared to conventional medicines. Plenty animal and clinical research are now available to prove the effectiveness and safety of herbo-mineral and medicinal plants in treating liver diseases.
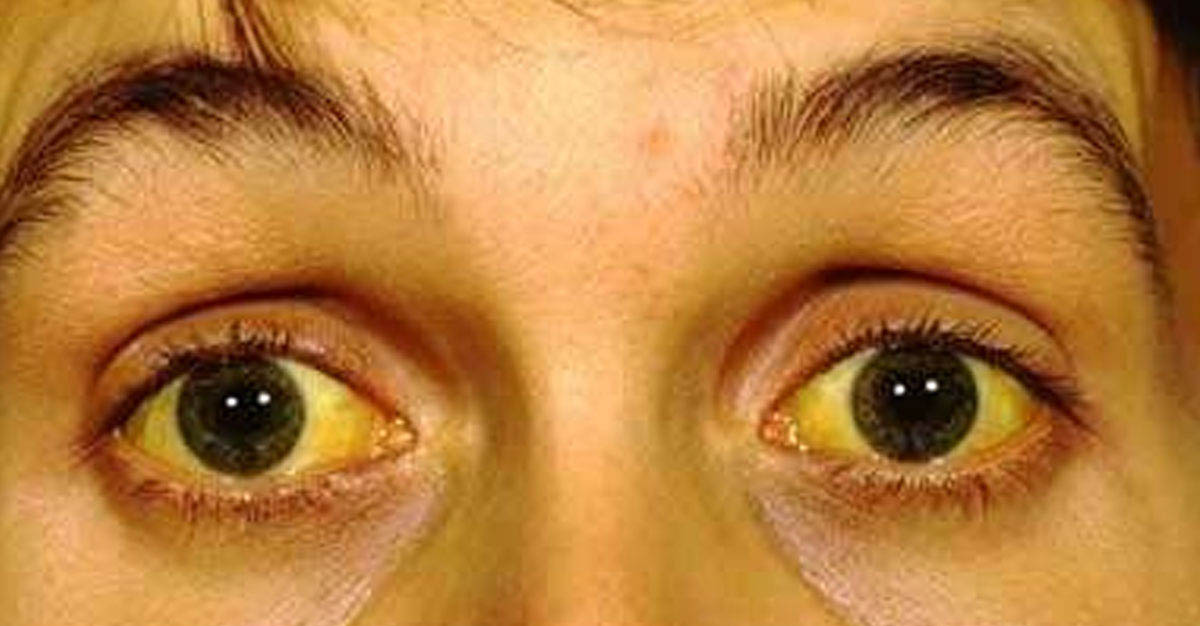
WHAT IS JAUNDICE?
Jaundice is a liver disease that is caused due to excess levels of bilirubin, a pigment present in the body. The most commonly observed jaundice symptom is yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. Excessive bilirubin levels can either be inherited or acquired. Inherited factors that are responsible for jaundice include glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and acquired factors include trauma and vitamin B 12 deficiency. Jaundice is diagnosed by measuring the bilirubin level in plasma. Consuming low-fat meals and plenty of water can help manage jaundice. In Ayurveda, Jaundice is known as Kamala. Personalized, root-cause Jaundice treatment has given relief to thousands of patients.
TYPES OF JAUNDICE
Jaundice is categorized into 3 types which is pre-hepatic, post-hepatic and hepatocellular.
1. Pre-hepatic Jaundice:
Pre-hepatic Jaundice is a situation in which Red Blood Cells breakdown in an excessive amount which profuse the process of liver to conjugate the bilirubin. Bilirubin which gets conjugated is excreted normally. Jaundice is caused by the remaining unconjugated bilirubin.
2. Hepatocellular Jaundice:
The dysfunction of hepatic Cells causes Hepatocellular Jaundice. In this situation the liver is no more able to conjugate bilirubin but sometimes it becomes cirrhotic, this leads to compression of the intrahepatic portion of the biliary tree which eventually leads to obstruction. The outcome of this is the mixing of conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin in the blood titled as mixed picture.
3. Post-Hepatic Jaundice:
It is the obstruction of biliary drainage. The secreted bilirubin is conjugated and this leads to hyperbilirubinemia.
CAUSES OF JAUNDICE
Jaundice occurs when there is too much bilirubin, a yellow-orange substance in your blood. It's found in your red blood cells and when these cells die, the liver filters it from the bloodstream and accumulates them so that they can pass through bile from the stools. But if something's wrong and your liver can't keep up, bilirubin builds up and can cause your skin to look yellow. This is caused due to liver infection.
Some of the reasons for jaundice in adults are:
- Hepatitis : Mostly viral, it may be short-lived or chronic. Drugs or autoimmune disorders can cause hepatitis. Over time, it can damage the liver and lead to jaundice.
- Acute inflammation of the liver: Due to the inflammation the ability of the liver to conjugate and secrete bilirubin, decreases and thus bilirubin quantity builds up. Inflammation is caused due to contaminated water or foods.
- Alcohol-related liver disease: If you drink too much over a long period of time-typically over 8-10 years-you could damage your liver. Two diseases, in particular, Alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis harm the liver.
- Hemolytic anemia: Due to this condition the production of the bilirubin increases in the body as large quantities of red blood cells get broken down.
- Gilbert's syndrome: In this condition the ability of the enzymes to process the bile excretion decreases. This is an inherited condition.
- Blocked bile ducts: These are thin tubes that carry a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine. Sometimes; they get blocked by gallstones, cancer, or rare liver diseases. If they do, they cause jaundice.
- Pancreatic Cancer: This is 10th most common cancer in men and 9th in women. It can block the bile duct and cause jaundice.
- Certain Medicines: Drugs like Acetaminophen, penicillin, birth control pills and steroids have been linked to liver disease.
SYMPTOMS OF JAUNDICE
What are the early symptoms of jaundice?
In many cases, the symptoms of jaundice are not usually seen. Its occurrence is noticed accidently as jaundice itself might be the underlying cause of some serious disease.
In case of mild jaundice, where it is seen for a short period of time with not much severity, the symptoms might include.
- Fever
- Yellow color to the skin and eyes, dark urine, and itchiness.
- Flu like symptoms
- Chills
- Dark coloured urine
- Grey coloured stool
- Change in skin colour
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain and some may have pain in upper abdomen due to inflammation of liver.
- Weight loss
- Vomiting and nausea
- The itchiness due to jaundice is sometimes so severe that patients scratch their own skin or experience insomnia.
If the cause of jaundice is something else than any infection the symptoms might also include itchy skin or weight loss. Sometime the reason behind the occurrence of jaundice is liver diseases. In that case, the symptoms might include.
- Chronic Hepatitis
- Acute Hepatitis
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
- Polyarthralgias
DIAGNOSIS
The correct diagnosis requires examinations and lab tests. Diagnosis includes history and physical exam and close attention to the abdomen, feeling for tumors, and checking the firmness of the liver. A firm liver indicates cirrhosis or scarring of the liver. A rock-hard liver suggests cancer. Several tests can confirm jaundice. First is a liver function test to find out whether the liver is functioning well or not.
Other supporting tests needed for diagnosis are:
- Bilirubin tests - A high level of unconjugated bilirubin compared to levels of conjugated bilirubin suggest hemolytic jaundice.
- Full blood count - This measures levels of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
- Hepatitis A, B and C tests - This test for a range of liver infections.
The doctor will examine the structure of the liver if they suspect an obstruction. In these cases, they will use imaging tests, including MRI, CT, and ultrasound procedures. They may also carry out an Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. This is a procedure combining endoscopy and X-ray imaging. Liver biopsy can check for inflammation, cirrhosis, cancer, and fatty liver.
COMPLICATIONS OF JAUNDICE
The itching in jaundice might get very intense and the patients might suffer from insomnia. The complications in jaundice are mostly not due to the jaundice itself, but the underlying causes. For example, a bile-duct obstruction jaundice might result in continuous bleeding due to vitamin deficiency.
In most common cases, the organs affected by jaundice are Liver, Gall bladder or Pancreas. Jaundice is the outcome of excessive breakdown of bilirubin in the body.
They causes leading this include:
- Excessive amount of Breakdown of Red Blood Cells breaking down and entering the liver.
- Damaging of the liver.
- The Bilirubin in the liver is facing problems in moving to the digestive tract.
Other organs which are affected by or are the venue of building jaundice are:
- A virus or parasite leading to infection of the liver
- Exposure to the drugs
- Blood Disorder
- Pancreas Cancer
- Chronic Liver Disease
- Pregnancy Jaundice
The risks which are associated with the development of jaundice are related either to the systemic or physiological abnormalities in the body or infections with viruses. Such conditions include the following:
- Chronic liver hepatitis.
- Viral infections like Acute conditions of hepatitis A, B or C or E or Epstein-Barr virus infection.
- Pyoderma gangrenosum - a skin disease condition.
- Joint inflammation diseases like polyarthralgia.
- Blockage conditions of the bile duct which may be due to gallstones or tumors.
- Genetic metabolic defects which is a rare condition.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Toxicity due to Certain medications like acetaminophen, oral contraceptives, and steroids.
- Hemolytic anemia.
AYURVEDA TREATMENT FOR JAUNDICE
Nidana parivarjana (avoiding the causative factors)
This therapy aims at keeping an individual free from disease by avoiding the causative factors of the disease and it is an essential part of Ayurvedic treatment in all diseases. The two-fold benefits of nidana parivarjana are:- (a) halting disease progression and (b) prevention of relapse. Based on the nidana (cause) of jaundice, preventive measures like avoiding eating at places with unclean food and water, using clean towels and good hygiene habits should be practised.
(I) VIRECHANA
The process of virechana helps in getting rid of the excess pitta from the body. Bitter purgatives like vibhandi (senna), ghrit Kumara (aloe) or amlaparni (rhubarb) are especially recommended in live diseases like jaundice. They clean the liver, decongest bile and remove any obstructions in the passage from which the bile flows. Virechana is beneficial in people with kapha dosha as they have high levels of bile in their body. Virechana is not always recommended in people with vata dosha as it weakens the digestive fire, which is naturally less strong in such people. It is also unadvisable in pregnant, old or weak individuals and those with a prolapsed stomach or uterus. Eranda taila (castor oil) may be used in the virechana process to treat jaundice. Medicines for pachana (digestion), deepana (increasing hunger), snehana (lubrication), and pittashamaka (pacifying pitta) are given as shaman chikitsa. The herbs used in the shaman chikitsa are mentioned in the next section.
(II) AYURVEDA MEDICATIONS
Phalatrikadi kwatha is a decoction made from eight herbs including haritaki (chebulic myrobalan), nimba (neem ), bhunimba (clearing nuttree), vibhitaki (belleric myrobalan), katuki, amalaki (amla ), guduchi (giloy, heart-leaved moonseed) and vasa (malabar nut). The kwatha (decoction) is bitter to taste and has pitta-rechaka (pitta removing), choleretic (stimulates the secretion of bile from the liver), cholagogue (promoting the discharge of bile from the system), and kapha-pitta shamaka (pitta and kapha pacifying) properties. It is useful in treating anaemia as well as jaundice. These properties help strengthen and stimulate the liver tissue thereby making phalatrikadii kwatha an excellent hepatoprotective (liver-protecting) drug. The ingredients also have antiviral and antioxidant properties, which just add to its protective and preventive action. Phalatrikadi kwatha can be taken for as long as two to three weeks or as directed by your physician.
Vasaguduchyadi kwatha Vasaguduchyadi kwatha is a renowned medicine in Ayurveda, which is used to treat many diseases including kamala. It is also used for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease and panduroga (anaemia). Vasaguduchyadi kwatha is a combination of haritaki, vasa (Malabar nut), nimb (neem), katuki, guduchi, chirayata (bitterstick), amalaki (Indian gooseberry), and vibhitaki. All of these herbs are rich in phytoconstituents like flavonoids, tannin-gallic acid, triterpenoids, coumarin glycosides and phenolic components, which have hepatoprotective properties. Vasaguduchyadi kwatha can be taken for as long as two to three weeks or as recommended by your ayurvedic doctor.
Punarnava mandoora Punarnava (spreading hogweed) mandoora can be taken for two to three weeks along with buttermilk or as directed by your physician. This medicine is known to have cough and fever-reducing, rejuvenating, anti-inflammatory (reduces inflammation), and diuretic properties. It is also used as a swedopaga medicine (as an adjunct to sweating therapy). Punarnava can also be used as a vegetable.
Arogyavardhini vati Arogyavardhini vati is one of the multidrug formulations used in treating liver disorders. The medicine aims to improve good health by achieving the balance in all doshas of the body.
This medication has antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties that help improve liver function. It clears body channels, stimulates digestive fire, balances fat distribution in the body and draws out toxins from the digestive system. Arogyavardhini vati is also available in the form of churna. The vati or churna can be taken for as long as two to three weeks with water, sugar cane juice, or honey as advised by your physician.
Dietary and lifestyle changes for jaundice as per ayurveda
(III) HERBS FOR JAUNDICE
Katuki (kutki) Katuki is known to have pittaghna (pitta-destroying) and kaphaghna (kapha-destroying) properties. Katuki is used in the deepena process of shamana chikitsa. It also stimulates liver function and helps in pitta removal and purgation. This is useful in reducing pitta and bile levels, thereby treating jaundice. Katuki is used in the form of a churna (powder) which can be taken with water, sugarcane juice, or honey or as recommended by your doctor
Kalamegha (king of bitters, green chirayta) Kalamegha is also used in the deepana process of shamana chikitsa. The properties of kalamegha are useful in treating chronic fever, removing pitta, inducing purgation and destroying worms. It also helps improve the function of spleenand digestive system. Kalamegha is available in the form of churna, which can be taken with water, sugarcane juice, or honey or as per the suggestion of your doctor.
Bhumyamalaki (Indian plum) Bhumyamalaki is known to be useful in many liver disorders like jaundice. It improves the overall health of liver and prevents hepatitis B virus infection. Bhumyamalaki can be taken in the form of juice or churna, which can be taken with water, sugarcane juice, or honey as per the recommendation of your doctor.
Garijara (wild carrot) Garijara is known to be a blood purifier and a nervine tonic in Ayurveda. It has been in use for jaundice treatment since a long time. Garijara isused in the snehana and deepana process of shamana chikitsa. It helps reduce pitta in the rakta dhatu and also pacifies vata dosha.
Take all medications and keep all appointments as recommended by your healthcare provider. Ayurvedic treatment varies from person to person and therefore one must consult an expert and not try these ayurvedic medicines for liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
DIET & LIFESTYLE FOR JAUNDICE
- Take complete rest.
- Include green gram , sugarcane juice, draksha (dried grapes), anjira (figs ), khichadi prepared from purana shali (oldrice), parwal (pointed gourd), haridra, barley, arahara (pigeon pea), wheat, pomegranates, papaya , potatoes, amla, buttermilk, grapes, mango, apple, cow's milk and adrak (ginger) in your diet.
- Water : Drink boiled and cooled water at least 8 glasses of water which helps the liver to flush out toxins. Also helps maintain a healthy weight and keeps the blood thin which helps to filter.
- Coffee or Herbal Tea : Moderate coffee consumption helps improve liver health
- Milk: High in antioxidants and also contains silymarin which helps repair damaged liver cells.
- Digestive Enzymes: Naturally occurring digestive enzymes may help reduce bilirubin. These are found in- Honey , Orange peels, Papaya, Pineapple, Mango
- Fruits and Vegetables: USDA recommends daily consumption of at least 2n ½ cups of vegetables and 2 cups of fruits. Healthy choices in jaundice include - Grapefruit, Avocado, Brussels sprouts, Grapes, Mustard greens
- Fibre : Especially soluble fibre helps move bile out of the liver, they can reduce toxicity. It is found in – Fruits, Vegetables, Legumes, Nuts, Whole grains.
- High fibre foods include - Cruciferous vegetables like kale and broccoli, Berries, Oatmeal, Almonds, Brown rice, Quinoa
- Consume fluids and water so as to keep well hydrated.
WHAT NOT TO EAT IN JAUNDICE?
Foods and drinks that must be avoided during jaundice are:
- Alcohol: Alcohol is the most dangerous of internal body tissues. It has heavily adverse effects on the liver.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Foods containing refined sugar such as Pasta, Soda, White bread and baked goods etc. must be avoided.
- Canned, Packaged and Smoked Food: Oily and fatty foods are difficult to digest which lead to many health problems.
- Beef, Pork and Fish: These kinds of foods contain amino acids which makes it difficult to digest and have a bad effect on the liver.
- Do not eat fried foods or pungent foods like chillies.
- Do not eat matar (peas), mustard oil, tambula (betel leaves ), sesame, excess oil and clarified butter, and urad (black gram)
PREVENTION OF JAUNDICE
- Do not drink excess water.
- Do not suppress natural urges.
- Do not sleep during the day.
- Avoid overexposure to the sun.
- Do not do excessive physical exercise.
- Ensure safe and healthy eating and drinking habits.
- During infection avoid fatty and oil rich foods.
- Avoid heavy alcohol use .
- Get vaccines for hepatitis.
- Take medications to prevent malaria before travelling to high risk areas.
- Avoid high risk behaviours like intravenous drug use or unprotected sex.
- Avoid potentially contaminated water/food and maintain good hygiene.
- Avoid medications that cause hemolysis in susceptible individuals.
- Consult the doctor immediately if one faces the symptoms of the jaundice.
- Opt for lean proteins
- Avoid Saturated fats
- Avoid Refined sugar
Take all medications and keep all appointments as recommended by your healthcare provider. Ayurvedic treatment varies from person to person and therefore one must consult an expert and not try these ayurvedic medicines for liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases.